
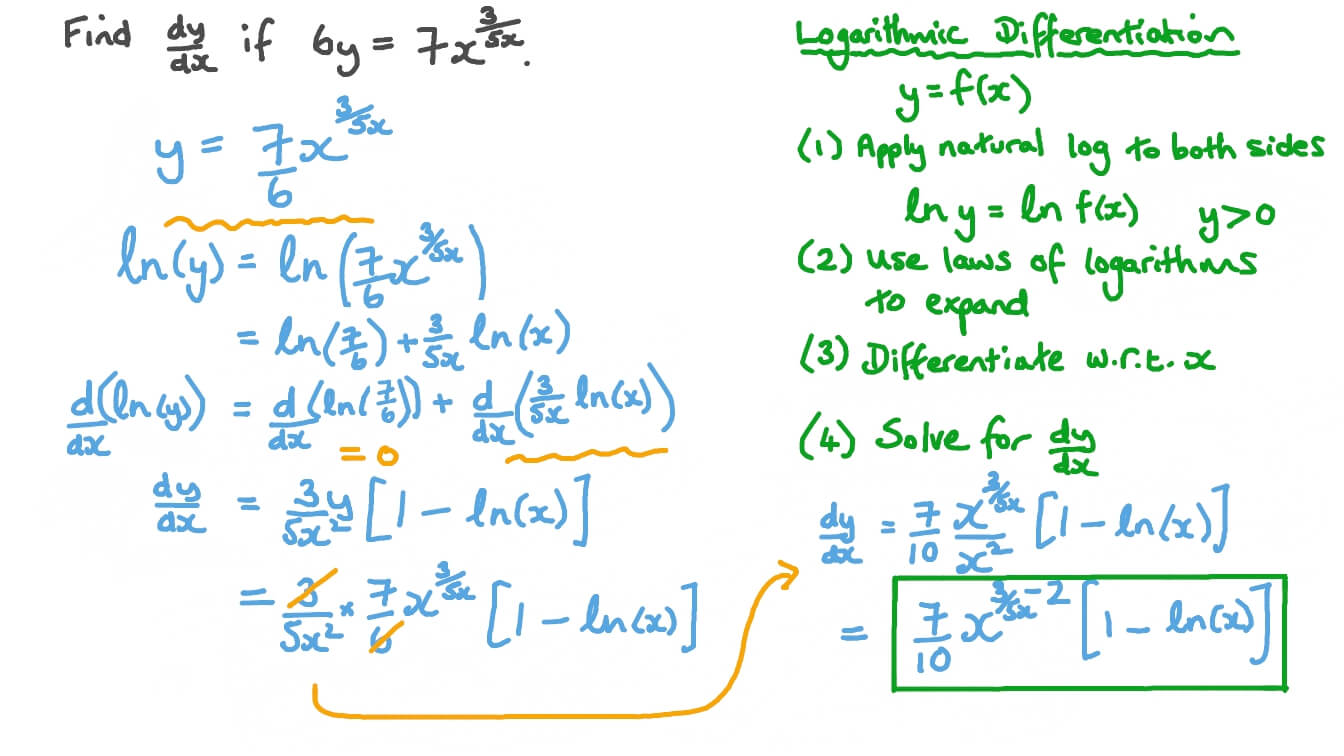
y log5 (x) y log 5 ( x) The derivative of log5(x) log 5 ( x) with respect to x x is 1 xln(5) 1 x ln ( 5). The common logarithmic function is written as ylog10x.

e e Notation: Summary x x dx d x a x dx d a 1, (ln ) ln 1 (log ) log e x ln x. Find the Derivative - d/dx y log base 5 of x. A function defined by ylogax,x>0, where xay,a>0, a1 is called the logarithm of x to the base a. First of all, consider the following equation: Equation. If the base is, we have Natural logarithm is the logarithm to the base. The log2 command was introduced in Maple 2021.įor more information on Maple 2021 changes, see Updates in Maple 2021. This means that we are going to use a different approach to proving the derivative of ln x ln x lnx. And the number (x) which we are calculating log base of (b) must be a positive real number. Please note that the base of log number b must be greater than 0 and must not be equal to 1.
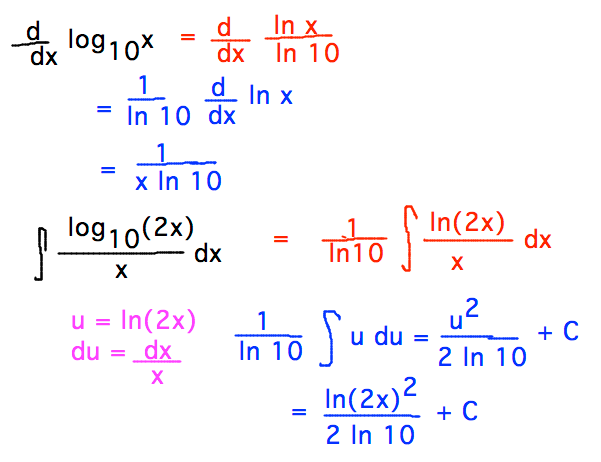
See exp for more about the exponential function. The logarithm log b (x) y is read as log base b of x is equals to y. Now, let’s go to your second question, which is Again, I’m going to try to answer this generally, for any base b. Similarly, e can also be entered as exp(1) in 1-D. If your log (x) refers to a logarithm with base e, as I think it does, then you find that the derivative is going to be 1/x from the formula above, as ln (e)1. The base can be entered as an index or as the second argument. You can enter the function log with base b using either the 1-D or 2-D calling sequence. For example, the function eX is its own derivative, and the derivative of LN(X) is 1/X. The default value of the base b is &ExponentialE. In particular, LOG means base-10 log in Excel. log is extended to general complex b and x by log b x = ln x ln b.
+Find+derivatives+for+f+(x)+%3D+5+ln+x+f+´(x)+%3D+5%2Fx.jpg)
Since 5 5 is constant with respect to x x, the derivative of 5 x 5 x with respect to x x is 5 d d x x 5 d d x x. Replace all occurrences of u u with 5 x 5 x. Its possible to define a logarithmic function logb(x) for any positive base b so that logb(e) f implies bf e. įor complex-valued expressions x, ln x = ln x + I arg x, where − π x = b y. The derivative of log 5 ( u) log 5 ( u) with respect to u u is 1 u ln ( 5) 1 u ln ( 5). We shall prove the formula for the derivative of the natural logarithm function using definition or the first principle method.The natural logarithm, ln, is the logarithm with base &ExponentialE = 2.71828.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
